What supplements should I take to lose weight?
This is the time of year when many of us are considering getting back to the gym and picking up more healthy habits. Among these, weight loss is a common health goal, so questions about weight loss supplements often come up.
In this article, we’ll discuss the different supplement categories that can support your weightFact checked by Nattha Wannissorn
Some of these supplements help with weight loss by supporting hormone balance, while others correct nutrient deficiencies, so you can continue using them after you’ve reached your goals.
Keep in mind that no dietary supplement can bypass the need for a caloric deficit through diet and exercise for weight loss.
Blood sugar-balancing supplements
Many people who carry extra weight struggle with insulin resistance, especially around the midsection. Insulin resistance can also contribute to excessive hunger and sugar cravings. Restoring insulin sensitivity, especially in the muscles, can help with fat loss. For this reason, supplements that support healthy blood sugar levels may help with weight loss.
Insulin is a hormone that takes glucose from the blood and into the cells for energy. High blood glucose levels can damage certain insulin receptors, such as Glut4, in muscle cells, making them unable to take up glucose. This unmetabolized glucose remains in the blood or travels to the liver or fat cells, where it will be converted to fat. This results in weight gain.
Better insulin sensitivity results in more glucose used by muscle cells rather than converted into fats. This can support healthy body composition.
Mitochondria are the cell’s “energy factories.” Some blood sugar-balancing supplements increase a process known as mitochondrial uncoupling (production of heat). The uncoupling of mitochondria can increase energy expenditure and thus help with weight loss.
If you are struggling with weight loss, even though you are dieting and exercising, try adding Blood Sugar Breakthrough. This supplement contains chromium which has been shown to regulate carbohydrate and fat metabolism, increase lean body mass, and support weight loss.
Synbiotics
Synbiotics are supplements that combine a mixture of probiotics and prebiotics. In the gut, these improve the activity and survival of “good” microorganisms. They thereby promote a healthy gut microbiome.
Synbiotics can help rebalance the gut bacteria and reseal the leaky gut.
Leaky Gut Guardian is a perfect and powerful combination of IgYmax and synbiotics that helps with balancing your gut microbiota and reducing intestinal permeability.
Magnesium
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in over 300 metabolic reactions in our body, including energy production.
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to various human diseases: poor heart health, excessive body fat and high blood sugar levels, respiratory issues, and mental health challenges.
A diet rich in magnesium is associated with a lower risk of high blood sugar due to magnesium’s role in glucose metabolism.
Further studies proposed that people with high body fat levels have low magnesium levels in their blood.
Since it is difficult to get the required dose of magnesium through diet alone, using magnesium supplements will ensure you get enough and help regulate glucose metabolism, thus helping with weight loss.
Vitamin D
Most of us know that vitamin D is important in bone health. However, vitamin D also plays a role in various other body processes.
For example, low vitamin D levels are associated with excessive body fat, high blood sugar levels, and heart health issues.
People with excessive body fat often have significantly lower blood levels of vitamin D. A possible cause is that fat tissue increases the clearance and uptake of vitamin D.
In one randomized study, 218 overweight women were on a weight loss program. Half received vitamin D supplementation with this program, and the other half were given a placebo. The women who were given vitamin D showed a greater improvement in weight loss.
Furthermore, overweight women who were given vitamin D for 12 weeks showed decreased body fat. However, they did not lose weight.
The conclusion is that vitamin D supplements can promote fat loss as long as a healthy diet and exercise are included.
Fat burners

Fat burners are typically non-nutritive supplements that:
- increase energy expenditure
- increase weight loss
- are involved in fat metabolism
- aid in fat oxidation during exercise
7-keto
7-keto-DHEA is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. This hormone assists with the burning of calories to produce body heat. Due to this property, 7-keto was seen as a potential supplement for weight loss.
30 individuals were put on an 8-week weight loss program: half received 7-keto and the other half a placebo. Individuals that received 7-keto lost significantly more weight (2.88 kg) than the placebo group (0.97 kg).
Furthermore, in another study, taking 7-keto increased the participants’ metabolism by 1.4%.
7-keto is a “fat burner” supplement that improves your metabolism and aids in weight loss, as long as it is followed by a healthy diet and exercise.
Innoslim
Innoslim is a natural fat burner made of extracts from Panax notoginseng and Astragalus membranaceus. It reduces fat by improving the metabolic environment. These supplements decrease the body’s absorption of glucose in the intestines by reducing an important glucose transporter called SGLT1. It then increases glucose absorption in muscle cells through increased glucose transport protein GLUT4.
These effects decrease the blood glucose levels and fat build-up in your body.
InnoSlim helps to lower blood sugar, lipids, and body fat. It may also help to reduce insulin resistance and inflammation. This may result in weight loss and lower blood sugar and insulin levels.
Appetite suppressants
Appetite suppressants are supplements and/or food that make you feel full, helping you to eat less.
Hoodia
Hoodia is a succulent plant long used by tribal people in Southern Africa as an appetite suppressant.
The evidence is scarce, and studies have mostly been done on rats, but hoodia seems to target both fat and muscle tissue to achieve weight loss. It works by tricking the brain into thinking you’ve eaten enough. Overweight individuals who ate hoodia showed greater weight loss improvement than those who were given a placebo.
Fenugreek
Fenugreek is a herb that is used as a weight-loss tool. It works as an appetite suppressant by causing those who take it to consume less fat and, therefore, fewer calories.
In a 6-week study, repeated administration of a fenugreek seed extract reduced the amount of fat healthy but overweight subjects ate by a small but substantial amount. Furthermore, it increased their feeling of fullness.
Bitter melon
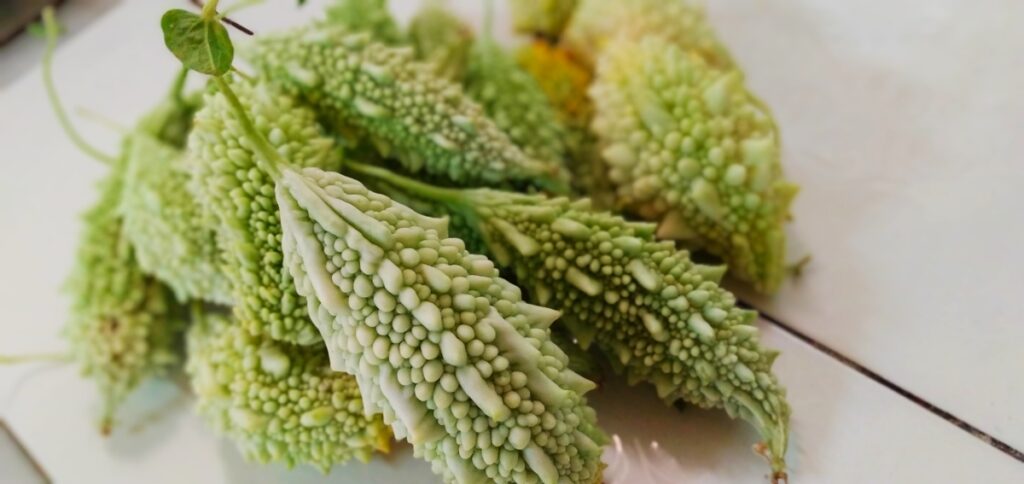

Bitter melon is a vine plant famous for its many beneficial properties. One of those properties is that it can reduce weight gain and insulin resistance.
In our bodies, bitter melon may boost the activity of proteins and certain receptors responsible for glucose regulation while decreasing fat production in adipose tissues and increasing fat breakdown.
Furthermore, bitter melon can suppress leptin – a hormone that helps the body maintain its weight.
Garcinia cambogia
Garcinia cambogia is a yellowish fruit with hydroxy citric acid, an ingredient beneficial for weight loss.
It works by either reducing appetite or blocking fat production in fat cells.
Coffee
Coffee is almost everyone’s favorite warm beverage, especially in the morning when we need that energy boost to kick-start our day.
Scientists have been exploring the correlation between drinking coffee and weight loss. A meta-analysis showed that higher coffee intake is associated with lower BMI and waist circumference.
Furthermore, in another meta-analysis, higher coffee intake correlated with a reduction in weight, BMI, and body fat.
Bottom line
Many supplements can promote and aid weight loss. Their mode of action ranges from increasing insulin sensitivity to blocking fat production in fat cells. These supplements not only aid in weight loss but can also have other beneficial effects on the body.
For instance, magnesium also improves the quality and quantity of sleep, vitamin D is good for our bones, and synbiotics help with gastrointestinal problems such as bloating.
Losing weight can be very difficult, especially around areas of the body where stubborn fat accumulates. Using supplements such as fat burners, appetite suppressants, and natural supplements can help you achieve your weight loss goals and improve your overall health.
Incorporating these supplements into your healthy diet and exercise regime will help improve your performance and results.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Subcommittee on Military Weight Management. Weight-Loss and Maintenance Strategies. National Academies Press; 2004.
- Insulin resistance. Diabetes.co.uk. Published January 15, 2019. Accessed September 23, 2021. https://www.diabetes.co.uk/insulin-resistance.html
- Freeman AM, Pennings N. Insulin Resistance. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Clamp LD, Hume DJ, Lambert EV, Kroff J. Enhanced insulin sensitivity in successful, long-term weight loss maintainers compared with matched controls with no weight loss history. Nutr Diabetes. 2017;7(6):e282.
- Schenk S, Harber MP, Shrivastava CR, Burant CF, Horowitz JF. Improved insulin sensitivity after weight loss and exercise training is mediated by a reduction in plasma fatty acid mobilization, not enhanced oxidative capacity: Weight loss, exercise training and insulin sensitivity. J Physiol. 2009;587(Pt 20):4949-4961.
- Mirabelli M, Russo D, Brunetti A. The role of diet on insulin sensitivity. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):3042.
- Demine S, Renard P, Arnould T. Mitochondrial uncoupling: A key controller of biological processes in physiology and diseases. Cells. 2019;8(8):795
- Ocloo A, Dongdem JT. Mitochondria as pharmacological targets: The discovery of novel anti-obesity mitochondrial uncouplers from Africa’s medicinal plants. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012;9(2):256-259.
- Anderson RA. Effects of chromium on body composition and weight loss. Nutr Rev. 1998;56(9):266-270.
- Malik JK, Ahmad AH, Kalpana S, Prakash A, Gupta RC. Synbiotics. In: Nutraceuticals. Elsevier; 2016:811-822.
- Mohammad S, Thiemermann C. Role of metabolic endotoxemia in systemic inflammation and potential interventions. Front Immunol. 2020;11:594150.
- Boutagy NE, McMillan RP, Frisard MI, Hulver MW. Metabolic endotoxemia with obesity: Is it real and is it relevant? Biochimie. 2016;124:11-20.
- Pendyala S, Walker JM, Holt PR. A high-fat diet is associated with endotoxemia that originates from the gut. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(5):1100-1101.e2.
- Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006;444(7122):1022-1023.
- Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature. 2009;457(7228):480-484.
- Fuke N, Nagata N, Suganuma H, Ota T. Regulation of gut Microbiota and metabolic endotoxemia with dietary factors. Nutrients. 2019;11(10):2277.
- Markowiak P, Śliżewska K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients. 2017;9(9):1021.
- Jiang L, Wang J, Liu Z, et al. Sodium butyrate alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by down-regulation of NF-κB, NLRP3 signaling pathway, and activating histone acetylation in bovine macrophages. Front Vet Sci. 2020;7:579674.
- Chakraborti CK. New-found link between microbiota and obesity. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015;6(4):110-119.
- Schwalfenberg GK, Genuis SJ. The importance of magnesium in clinical healthcare. Scientifica (Cairo). 2017;2017:4179326.
- Jahnen-Dechent W, Ketteler M. Magnesium basics. Clin Kidney J. 2012;5(Suppl 1):i3-i14.
- Razzaque MS. Magnesium: Are we consuming enough? Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1863.
- Magnesium. Nih.gov. Accessed September 23, 2021. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/
- Toprak O, Kurt H, Sarı Y, Şarkış C, Us H, Kırık A. Magnesium replacement improves the metabolic profile in obese and pre-diabetic patients with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease: A 3-month, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2017;42(1):33-42.
- Hassan SAU, Ahmed I, Nasrullah A, et al. Comparison of serum magnesium levels in overweight and obese children and normal weight children. Cureus. 2017;9(8):e1607
- Park JE, Pichiah PBT, Cha Y-S. Vitamin D and metabolic diseases: Growing roles of vitamin D. J obes metab syndr. 2018;27(4):223-232.
- Shamik J. Parikh, Marni Edelman, Gabriel I. Uwaifo, Renee J. Freedman, Mariama Semega-Janneh, James Reynolds, Jack A. Yanovski. The Relationship between Obesity and Serum 1,25-Dihydroxy Vitamin D Concentrations in Healthy Adults. J Clinic Endocri & Metabol. 2004;89(3):1196–1199. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031398
- Liel Y, Ulmer E, Shary J, Hollis BW, Bell NH. Low circulating vitamin D in obesity. Calcif Tissue Int. 1988;43(4):199-201.
- Mason C, Xiao L, Imayama I, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation during weight loss: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(5):1015-1025.
- Salehpour A, Hosseinpanah F, Shidfar F, et al. A 12-week double-blind randomized clinical trial of vitamin D₃ supplementation on body fat mass in healthy overweight and obese women. Nutr J. 2012;11(1):78.
- Jeukendrup AE, Randell R. Fat burners: nutrition supplements that increase fat metabolism: Fat burners. Obes Rev. 2011;12(10):841-851.
- Cleary MP. The antiobesity effect of dehydroepiandrosterone in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991;196(1):8-16.
- Lardy H, Kneer N, Bellei M, Bobyleva V. Induction of thermogenic enzymes by DHEA and its metabolites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995;774(1 Dehydroepiand):171-179.
- Kaiman DS, Colker CM, Swain MA, Torina GC, Shi Q. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 3-acetyl-7-oxo-dehydroepiandrosterone in healthy overweight adults. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2000;61(7):435-442.
- Zenk JL, Frestedt JL, Kuskowski MA. HUM5007, a novel combination of thermogenic compounds, and 3-acetyl-7-oxo-dehydroepiandrosterone: each increases the resting metabolic rate of overweight adults. J Nutr Biochem. 2007;18(9):629-634.
- InnoSlim® – Weight management. Nulivscience.com. Accessed September 23, 2021. https://nulivscience.com/ingredients/innoslim
- Challenging insulin resistance & supporting metabolic efficiency with InnoSlim®. Nulivscience.com. Accessed September 23, 2021. https://nulivscience.com/blog/insulin-resistance-metabolic-efficiency-innoslim
- Roza O, Lovász N, Zupkó I, Hohmann J, Csupor D. Sympathomimetic activity of a Hoodia gordonii product: a possible mechanism of cardiovascular side effects. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:171059.
- Perna S, Infantino V, Peroni G, et al. Effects of Hoodia Parviflora on satiety, abdominal obesity and weight in a group of overweight subjects: a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2020;66(3):211-218.
- Chevassus H, Gaillard J-B, Farret A, et al. A fenugreek seed extract selectively reduces spontaneous fat intake in overweight subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;66(5):449-455.
- Mathern JR, Raatz SK, Thomas W, Slavin JL. Effect of fenugreek fiber on satiety, blood glucose and insulin response and energy intake in obese subjects: Fenugreek fiber and satiety. Phytother Res. 2009;23(11):1543-1548.
- Bao B, Chen Y-G, Zhang L, et al. Momordica charantia (Bitter Melon) reduces obesity-associated macrophage and mast cell infiltration as well as inflammatory cytokine expression in adipose tissues. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84075.
- Alam MA, Uddin R, Subhan N, Rahman MM, Jain P, Reza HM. Beneficial role of bitter melon supplementation in obesity and related complications in metabolic syndrome. J Lipids. 2015;2015:496169.
- Chuah LO, Ho WY, Beh BK, Yeap SK. Updates on antiobesity effect of Garcinia origin (-)-HCA. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:751658.
- Ohia SE, Opere CA, LeDay AM, Bagchi M, Bagchi D, Stohs SJ. Safety and mechanism of appetite suppression by a novel hydroxycitric acid extract (HCA-SX). Mol Cell Biochem. 2002;238(1/2):89-103.
- Hayamizu K, Ishii Y, Kaneko I, et al. Effects of garcinia cambogia (Hydroxycitric Acid) on visceral fat accumulation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2003;64(8):551-567.
- Lee A, Lim W, Kim S, et al. Coffee intake and obesity: A meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2019;11(6):1274.
- Tabrizi R, Saneei P, Lankarani KB, et al. The effects of caffeine intake on weight loss: a systematic review and dos-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(16):2688-2696.






