Zonulin

Leaky gut can cause chronic inflammation and suboptimal performance. Zonulin is a protein that can go up when you have a leaky gut. This article will introduce zonulin and how you can address high blood zonulin.
What Is Zonulin?
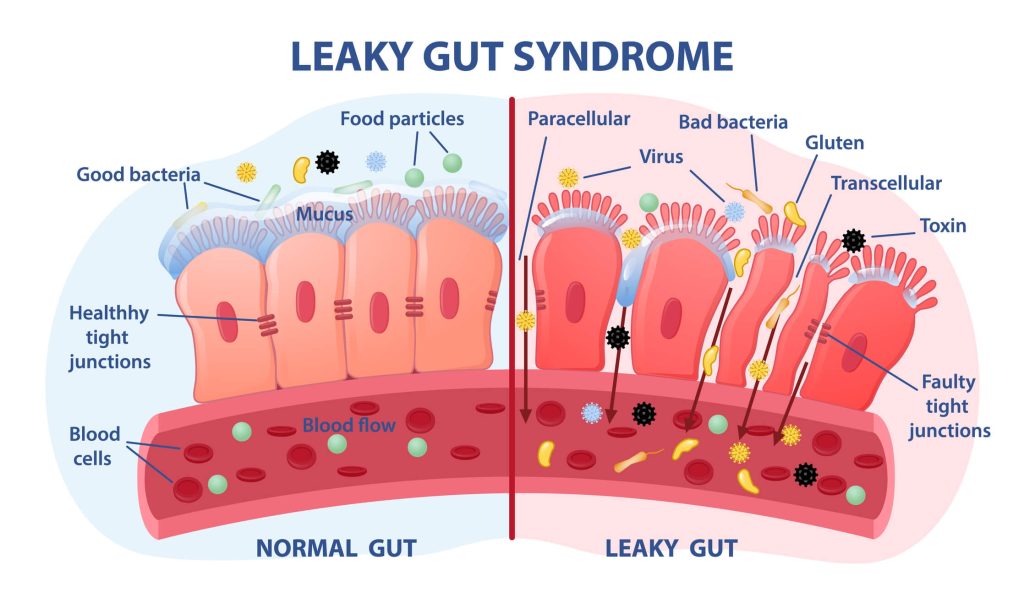
Zonulin is a family of proteins that regulate tight junctions (TJ) between intestinal cells. TJ proteins are necessary to maintain a strong gut barrier. When these proteins are damaged, the barrier becomes leaky. Leaky gut is associated with increased inflammation and all kinds of related health conditions.
Your gut lining cells release zonulin in response to certain foods or microbes. Release of zonulin reduces intestinal TJ proteins and may cause leaky gut syndrome. It also causes inflammation and the movement of immune cells from the gut into the body. Conversely, long-term zonulin elevation may cause leaky gut.
One of the most potent triggers of zonulin is bacterial overgrowth and gut flora imbalance (dysbiosis). This is one of the ways that dysbiosis contributes to leaky gut.
Aside from dysbiosis, gluten is the other most powerful stimulator of zonulin release.
What Does High Zonulin Mean?
High zonulin levels are associated with leaky gut and therefore, many chronic inflammatory conditions.
Chronic inflammation and other conditions associated with elevated zonulin levels include:
- Autoimmunity (multiple sclerosis, Chron’s, Type 1 diabetes, etc.)
- Celiac disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- Autism
- ADHD
- Depression
- Schizophrenia
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Testing for zonulin however, is not perfect and does not always correlate with the presence of leaky gut or disease.
Problems With Zonulin Testing
Zonulin was first discovered as a gut response to the bacteria Vibrio cholera. A zonulin test called enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed. ELISA testing is a method where a tray is used that has molecules in it that recognizes and sticks to the substance being tested.
The lab sample is placed in the tray. A machine then calculates how much of the substance, in this case zonulin, is present based on how much binds to the ELISA molecule. The trouble with zonulin ELISA testing is that the original “sticky” molecule developed doesn’t effectively measure zonulin.
In short, zonunlin tests currently available don’t appear to actually measure zonulin. They measure something related to zonulin, like a precursor or another related molecule. Scientists are still trying to figure that part out.
Testing for zonulin may be helpful as part of a broader plan to examine gut health, but it is not always enough to diagnose leaky gut on its own. That means it’s totally possible to have normal zonulin levels and all the symptoms of leaky gut, suggesting that you should repair your gut anyway.
How To Reduce/Repair Zonulin
The first step to reduce zonulin levels is to decrease, or eliminate, the triggers for its release. The most likely contributors to elevated zonulin are gut flora imbalance and food sensitivities.
Balance Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis triggers inflammation and zonulin release from gut cells. These both contribute to the development of leaky gut.
Gut flora can become imbalanced due to factors such as:
- Antibiotic use
- Gut infections
- High alcohol intake
- Inflammatory diet
- Low fiber intake
There are a variety of approaches to balance your gut flora, depending on the nature and severity. If you have small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), you may need a more holistic and intensive approach. Whereas other milder imbalances may be addressed with one or two methods.
Approaches for establishing healthy gut flora balance include:
- Probiotics
- Prebiotics (inulin, resistant starch, pectin, etc.)
- Herbal antimicrobials (garlic, clove, oregano, etc.)
- Anti-inflammatory diet
- FODMAP diet
It contains:
- Science-based probiotic strains
- Prebiotics
- Natural antioxidants
- Immune modulating antibodies that can bind and escort out bad bacteria
- Glutamine rich collagen
Biome Breakthrough rebalances your gut flora, modulates inflammation, and helps repair a leaky gut barrier.
Eliminate Gluten
Gluten, being one of the most potent triggers for zonulin release, is an important protein to eliminate. Gluten appears to affect everyone a little differently. Those who are sensitive have stronger inflammatory reactions.
Regardless of if you have a gluten sensitivity or not though, gluten will trigger zonulin release to some extent. If you have digestive problems, inflammatory issues, or elevated zonulin, you may want to consider complete gluten elimination.
It doesn’t take a lot of gluten to cause trouble in very sensitive people. Even milligrams of gluten, which is not visible to the naked eye, can trigger reactions.
Gluten Guardian contains 6 plant-based proteolytic enzymes, including Peptidase DPP-IV that helps break down gluten. If you’re gluten-sensitive or Celiac, it doesn’t allow you to eat bread or full plates of pasta, but it may help in cases of minor accidental exposure, especially in restaurants that also handle wheat products.

Remove Food Sensitivities
Many people react to certain foods with an immune and inflammation reaction in their gut. These are known as food sensitivities. Removing these may reduce zonulin levels and inflammation.
The easiest way to discover food sensitivities is the elimination-rechallenge diet. Suspected foods are eliminated for at least 2, ideally 4 weeks. You should see symptoms improve if a food sensitivity was removed. Then, reintroduce one food at a time, for a day each, and wait three days to see if your symptoms return. If symptoms return after eating a reintroduced food, the symptom is likely causing inflammation and should be removed permanently.
Common food sensitivities include:
- Soy
- Dairy
- Wheat
- Gluten
- Corn
- Potatoes
- Eggs
- Nightshade family (tomatoes, peppers, etc.)
Colostrum Bovinum
Colostrum bovinum is derived from cow milk. Colostrum is produced in the early days of milk production after a calf is born. It is particularly high in immune antibodies. Supplementation with colostrum bovinum strengthens the gut barrier and decreases zonulin levels.
Vitamins A And D
Both vitamin A and D play important roles in healthy immune system function. They also contribute to maintenance of tight junctions and a strong gut barrier. Supplementation with vitamin A and D may decrease zonulin levels and help repair leaky gut.
Conclusion
Zonulin family proteins regulate the integrity of your gut barrier. While testing is not perfect, it can provide a window into potential leaky gut issues. If your zonulin is high, or you suspect you have leaky gut syndrome, start building healthy gut flora, and removing food sensitivities, including gluten. This will get you on the right track to improving digestive health and inflammation symptoms.
- Tajik N, Frech M, Schulz O, et al. Targeting zonulin and intestinal epithelial barrier function to prevent onset of arthritis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1995. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15831-7
- Fasano A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Res. 2020;9:69. doi:10.12688/f1000research.20510.1
- Massier L, Chakaroun R, Kovacs P, Heiker JT. Blurring the picture in leaky gut research: how shortcomings of zonulin as a biomarker mislead the field of intestinal permeability. Gut. 2021;70(9):1801-1802. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323026
- Hałasa M, Maciejewska D, Baśkiewicz-Hałasa M, Machaliński B, Safranow K, Stachowska E. Oral supplementation with bovine colostrum decreases intestinal permeability and stool concentrations of zonulin in athletes. Nutrients. 2017;9(4):370. doi:10.3390/nu9040370
- Xiao L, Cui T, Liu S, et al. Vitamin A supplementation improves the intestinal mucosal barrier and facilitates the expression of tight junction proteins in rats with diarrhea. Nutrition. 2019;57:97-108. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2018.06.007




